How To Handle Constructors In A Class With A Template In C++
Modernistic C++ course members and initializations the right way
Using In-member initialization, using constructors smartly and using class members functions in a safety and proper mode to avoid mistakes

Table of Contents
- Employ member initializers in the same order as their announcement
- Prefer in-class fellow member initializer over constant initializations OR over default constructor.
- Don't bandage away const, ever!
- Use delegating constructors to represent common deportment for all constructors of a class.
1. Employ member initializers in the same order equally their declaration
Member variables are always initialized in the order they are declared in the course definition.
The gild in which you write them in the constructor initialization listing is ignored 🥴
Make certain the constructor lawmaking doesn't confusingly specify dissimilar orders. For e.g. this instance as below —

email is declared before first_name and last_name in the class definition, hence as per the constructor call, it will be initialized kickoff and will attempt to apply the other not-nonetheless-initialized fields which are first_name and last_name .
How to arrive right
This code harbors a bug that's as subtly harmful as it is difficult to spot hence
Write fellow member initializers in the same order equally their declaration
Many compilers (simply non all) will effect a warning if you break this dominion. Modern compilers Clang, MSVC detect it with the right use of right warning flags.
Reason
The reason for this linguistic communication blueprint decision is to ensure there is a unique order to destroy members; otherwise, the destructor would have to destroy objects in unlike orders, depending on the constructor that built the object.
Do good
- Protects yous from an oddity of the language without requiring anybody to know it.
- Might encourage yous to rethink your form pattern so this dependency goes abroad
2. Prefer in-class fellow member initializer over constant initializations OR over default constructor
Yous should don't define a default constructor that only initializes data members; utilise in-class member initializers instead which works as a practiced fallback in case y'all forget to initialize something.
Example — A bad class that misses one initialization in a constructor
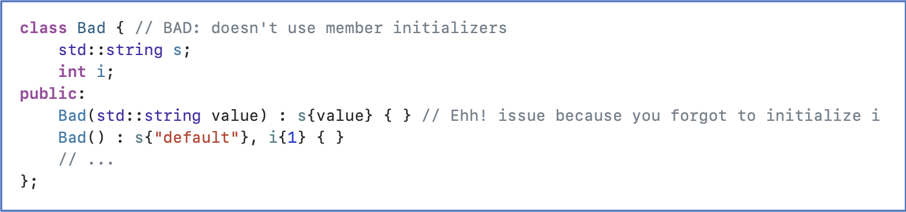
where the following is an example of a much ameliorate form

Reason
Using in-form fellow member initializers lets the compiler generate the function for you. Also, the compiler-generated function can be more efficient 😊
Benefits
- No overhead of taking care of initializing constants separately in each constructor.
- Functioning gain by using standard default constructors.
3. Don't cast abroad const, ever!
We shouldn't cast away from getter functions even when there seems a need.
For e.thou. — Stuff is a form that does some calculations overnumber1 and number2 and computes the result. Now getValue() const is a function that fetches the value, and being a getter function is marked const.
number1 and number2 are updated byService1() and Service2() functions respectively.

Now, in case read frequency of getValue() is much more than the number of writes, nosotros should preemptively update the cachedValue which is returned.
Such as —

All the same, in instance the number of writes is much more, we should follow a lazy calculation approach where nosotros gear up a dirty flag such as beneath —

But this poses a problem considering const office can non modify this newly introduced class fellow member variable cachedValid .
- A wrong fix would be to remove const from
getValue()function - Another wrong fix would exist to
const_castover "this" arrow.
Reason
Doing this makes a lie out of const. Any variable is actually declared asconst, modifying it may result in undefined behavior.
- Allows
getValue()function to modify anything in the example. - The header file is now speaking a prevarication basically.
Correct Fix
The correct prepare would be to declare cachedValid and cachedValue as mutable so that thegetValue() function can merely alter the mutable ones.

Benefits of correct gear up
- Header file tells the truth
-
getValue()function can only change the mutable variables - Code accessing mutable members is shorter and more than readable
- Easier to write, read, and maintain
- Const-correctness may enable optimizations 😊
iv. Utilize delegating constructors to correspond common deportment for all constructors of a class
The common activeness gets slow to write and may accidentally not be common. Hence, wherever possible we should refer to existing constructors.
For eastward.1000. — This Date is a bad course.


Reason
To avoid repetition and accidental differences.
Cheers for reading this article! Feel costless to go out your comments and let me know what you think. Delight experience free to driblet any comments to improve this article.
Please check out my other articles and website, Have a great day!
Please feel gratuitous to purchase me a java ☕ => HERE
How To Handle Constructors In A Class With A Template In C++,
Source: https://medium.com/pranayaggarwal25/using-modern-class-members-and-initializations-c11e931c3ba
Posted by: bishopknoton.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Handle Constructors In A Class With A Template In C++"
Post a Comment